JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an engine that provides a runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed. It converts source code to bytecode and then it will execute your program.
What it does
- Loads code
- Verifies code
- Executes code
- Provides runtime environment
JVM Architecture
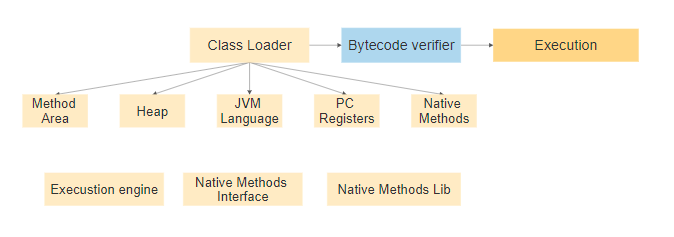
- ClassLoader -: Used for loading java class
- Method Area-: Used For storing class structures
- Heap-: To store Objects their related instance like variables, and arrays
- JVM language Stacks-: Store only local variables
- PC Registers-: Used for storing the address of the Java virtual machine instruction
- Native Method Stacks-: it hold the instruction of native code
- Execution Engine-: This is software and used to test hardware to execute program
- Native Method interface-: Interface is a programming framework it allows your java to run in JVM
- Native Method Libraries-: It contains collection of the Native Libraries
Let's see an example to print the classloader name
public class JavaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c = JavaApplication.class;
System.out.println(c.getClassLoader());
System.out.println(String.class.getClassLoader());
}
}
Output:
| run:
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@73d16e93 null |
Thanks, May this will help you.